GhostDrift Mathematical Institute: Official Statement on Scope and Positioning
- kanna qed
- 1月27日
- 読了時間: 7分
1. Organizational Identity
GhostDrift Mathematical Institute is a research institution dedicated to designing next-generation intellectual infrastructure.
In an era characterized by Generative AI, automated decision-making, and complex social systems, we mathematically anchor the preconditions of "who is responsible, based on what, and to what extent"—questions that inevitably arise at the locus of decision-making. We design these preconditions to be strictly verifiable by third parties.
This design does not propose a proprietary philosophy or arbitrary rules. Rather, it is positioned as a logical necessity derived from the synthesis and structuring of prior research in mathematics, computer science, information retrieval, and optimization theory.
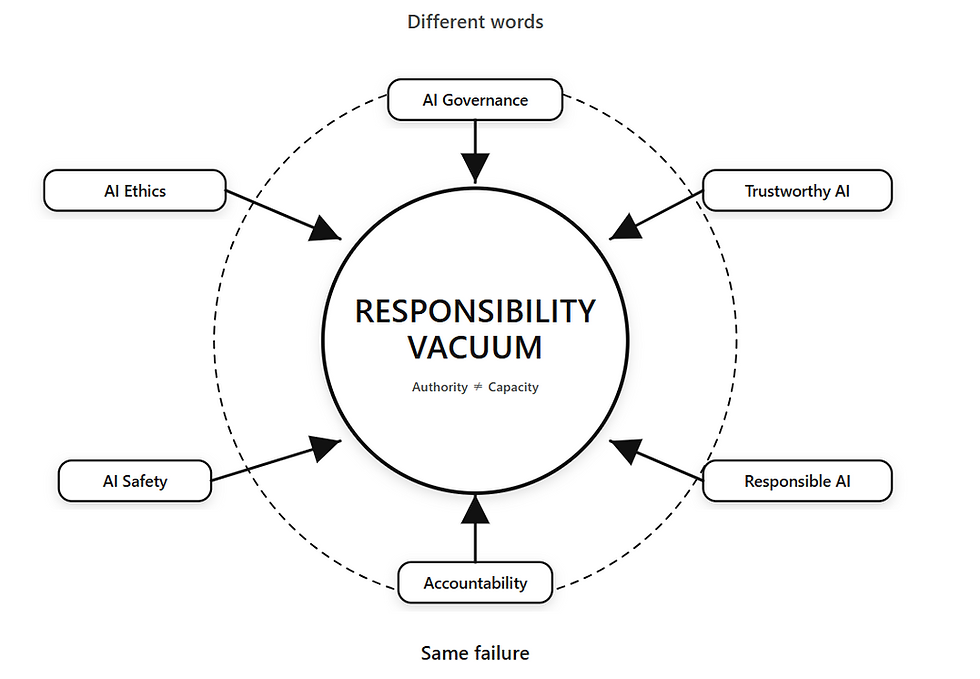
In the current societal landscape, Big Tech companies implement models and products that "alter societal preconditions," while regulatory and standardization bodies (EU, ISO, etc.) provide frameworks to evaluate organizational structures and model safety.
GhostDrift occupies a distinct scope: the layer of "mathematically fixing preconditions for individual operational decisions (transactions) in advance, ensuring they can be validated as PASS/FAIL by third parties."
We do not provide model performance evaluations or organizational governance certifications. Instead, we define the "conditions for a judgment to be established as legitimate" for each individual transaction, and the "boundaries of liability (conditions for cessation/approval)" to prevent the evaporation of responsibility should those preconditions collapse. These are defined as a mathematical protocol that renders post-hoc alteration impossible (immutable).
2. Theoretical Framework: Algorithmic Legitimacy Shift (ALS)
We employ Algorithmic Legitimacy Shift (ALS)—the phenomenon where the legitimacy of judgment is irreversibly shifted from humans to algorithms due to the proliferation of generative search and answer engines—as an analytical label within this document<sup id="fn-als-text">[†]</sup>.
ALS serves not as a mandatory prerequisite for our existence, but as an analytical label for describing the environment based on observation logs. Even if the nomenclature of ALS or the evaluation of its irreversibility is disputed, the necessity to fix the legitimacy conditions of individual decisions in advance—and to enable third-party binary verification—remains valid.
We utilize ALS as a coordinate system to describe the topological difference (phase difference) between Big Tech (those altering the premise), Regulations/Standards (those providing frameworks), and Operational Decisions (Transactions). In situations where this type of environmental change is observed, traditional configurations of accountability tend to erode. GhostDrift constructs mathematical models to prevent the evaporation of responsibility, independent of the presence or absence of such environmental changes.
<small id="fn-als-note">[†] External observations of the analytical label "ALS" (records including timestamps, queries, and generation results) are attached as primary source material in the separate Technical Document.</small>
3. Summary of Objective Comparison: A Map of the
"Phase" of Activity
The distinction of GhostDrift Mathematical Institute lies not in competition with existing research institutions or evaluation bodies, but in the difference of "the phase (layer) of the problem addressed" and the "target of evaluation."
A detailed comparative investigation (see "Appendix" below) has clarified the following structural differences:
Difference in Evaluation Target:
Regulations/Standards (EU AI Act, ISO): Primarily target "organizational structures," "risk management processes," and "model capabilities."
GhostDrift: Targets the conditions for the establishment of legitimacy for each "Operational Decision (Transaction)."
Strength of Fixing and Verifiability:
Guidelines/Frameworks (NIST, ATIH): Provide flexible guidance, intentionally leaving room for interpretation.
GhostDrift: Fixes conditions as post-hoc-impossible (Immutable) mathematical terms and provides protocols that allow third parties to render a binary (PASS/FAIL) verdict.
GhostDrift fills the "critical gap" of "fixing preconditions for operational decisions" within existing systems and technologies, playing a complementary role to established evaluation frameworks.

[Appendix] GhostDrift Mathematical Institute Objective Comparison Report
1. Overview and Methodology
1.1 Purpose
The purpose of this study is to objectively map the position (phase) of GhostDrift Mathematical Institute's (GD) approach compared to existing major AI-related organizations and systems, based strictly on published primary information.
1.2 Strict Adjudication Criteria
To ensure objectivity, the following strict criteria were adopted. No adjudication based on inference is performed.
Addressed (●): Primary sources (official documents, legal texts, specifications) explicitly state descriptions meeting the requirements of the axis.
Explicitly Excluded (×): Primary sources explicitly state that the item is "not covered," "out of scope," or "not performed."
Fundamentally Excluded (-): Applied only when the definition of the entity (e.g., basic research only) is logically incompatible with the function, as derivable from primary sources.
Not Applicable / Indeterminate (N/A): Cannot be determined from public information or no explicit description exists. "Not written" is not assumed to mean "not done"; all such cases are marked as N/A.
1.3 Definition of Comparison Axes (Granular)
To eliminate ambiguity, each axis was decomposed into observable elements for adjudication.
Axis 1: Precondition Fixing (Transaction Level)
Does it define the conditions under which an individual transaction (decision) is considered legitimate, rather than the organization or model as a whole?
Axis 2: Third-Party Binary Verdict (Independent & Binary)
(2a) Is the adjudicating entity an independent third party?
(2b) Is the result designed as a clear binary (PASS/FAIL)?
Axis 3: Immutability (Technical Fixing)
(3a) Is the immutability of logs and decision conditions explicitly stated as a technical requirement (signatures, hashes, etc.)?
(3b) Are verification procedures for third parties demonstrated?
2. Comparative Survey Results
Entity Name (Type) | Primary Evaluation Target | 1. Precondition Fixing(Transaction Level) | 2. Third-Party Verdict(Independent & Binary) | 3. Immutability(Technical Fixing) |
Institute for Advanced Study (Fundamental Research) | Theory / Truth | N/A <sup>[1]</sup> | N/A | N/A |
Max Planck Society (Fundamental Research) | Basic Science | N/A <sup>[2]</sup> | N/A | N/A |
OpenAI / DeepMind (Applied AI Lab) | Model Capabilities/Safety | N/A <sup>[3]</sup> | N/A <sup>[4]</sup> | N/A |
EU AI Act (Regulation) | High-Risk AI Systems | N/A <sup>[5]</sup> | ● <sup>[6]</sup> | N/A |
ISO/IEC 42001 (Standard) | Management Systems | N/A <sup>[7]</sup> | ● <sup>[8]</sup> | N/A |
NIST AI RMF (Framework) | Risk Management Process | × <sup>[9]</sup> | × <sup>[10]</sup> | N/A |
UK AISI (Gov Eval Institute) | Model Safety | N/A | N/A <sup>[11]</sup> | N/A |
GhostDrift Mathematical Institute (Math Infra) | Conditions of Legitimacy | ● <sup>[12]</sup> | ● <sup>[13]</sup> | ● <sup>[14]</sup> |
Sources and Rationale (Based on Primary Materials)
[1] Institute for Advanced Study (IAS): Positioning as a Basic Research Institution (N/A)
Primary Source: IAS – Mission & History
Rationale: Explicitly states "curiosity-driven basic research." Specification of educational or operational infrastructure requirements is out of scope (Thus N/A for this axis).
[2] Max Planck Society: Focus on Basic Research (N/A)
Primary Source: Max Planck Innovation – MPR 2020 (PDF)
Rationale: States "Insight must precede application," clarifying the focus on basic research (No description of operational decision protocols -> N/A).
[3] OpenAI: Conducting Safety Evaluations (System Card / evaluation) (But not Transaction-level fixing -> N/A)
Primary Source: OpenAI – Safety Evaluations Hub
Auxiliary Source: GPT-4o System Card
Rationale: While model safety evaluations are published, there is no explicit system specification for an external third party to fix preconditions and PASS/FAIL each operational decision (Transaction) (N/A).
[4] Google DeepMind / Google: Model Cards and Evaluation Guides exist (But not independent third-party operational PASS/FAIL -> N/A)
Primary Source: Gemini 2.5 Pro – Model Card (PDF)
Auxiliary Source: Google – Model Cards
Rationale: Evaluations and safety performance are presented, but no system specification is explicitly stated for independent third-party binary adjudication for each operational transaction (N/A).
[5] EU AI Act: Evaluation Target is Conformity of "High-Risk AI Systems" (Not Transaction-level -> N/A)
Primary Source: EU AI Act Service Desk – Article 43 (Conformity assessment)
Rationale: Conformity assessment is a system at the "system/product" layer; targeting individual inference units (Transactions) during operation is not central to the text of the article (Thus Axis 1 is N/A).
[6] EU AI Act: Third-Party Conformity Assessment including Notified Bodies (●)
Primary Source: EU AI Act Service Desk – Article 43
Relevant Text: "provider may choose any of the notified bodies," explicitly stating a framework for conformity assessment involving third-party bodies (●).
[7] ISO/IEC 42001: Target is "AI Management System (AIMS)," not Individual Decisions (N/A)
Primary Source: ISO – ISO/IEC 42001:2023
Rationale: A standard targeting internal AIMS (policies, objectives, processes), not specifications for adjudicating operational transactions (Axis 1 is N/A).
[8] ISO/IEC 42001: Has a Framework for Third-Party Certification (Conformity/Non-Conformity) (●)
Primary Source: ISO – ISO/IEC 42001:2023
Rationale: Structured as a requirements standard allowing for third-party certification (conformity) operations, possessing a binary (conformity/non-conformity) framework (●).
[9] NIST AI RMF: Explicitly "non-prescriptive / outcome-focused" (×)
Primary Source: NIST AI RMF 1.0 (PDF)
Relevant Text: Explicitly states "Be outcome-focused and non-prescriptive." Designed not to enforce fixed criteria (×).
[10] NIST AI RMF: Voluntary Use (×)
Primary Source: NIST AI RMF 1.0 (PDF)
Rationale: Premised on voluntary use; mandatory implementation as a third-party binary adjudication protocol is not the design objective (×).
[11] UK AI Safety Institute: Explicitly states Evaluation "does not constitute a pass/fail test or mandate conditions" (N/A)
Primary Source: UK Government – Introducing the AI Safety Institute
Relevant Text: "This does not constitute a pass/fail test or mandates conditions for deployment." (Confirmed as not being a binary adjudication system for operational gates -> N/A).
[12] GhostDrift: Mission explicitly states "Fixing Preconditions for Operational Decisions" (●)
Primary Source: About GhostDrift (Institute Official)
Rationale: Explicitly includes the objective of mathematically fixing the preconditions for legitimacy that arise at the point of decision-making (Transaction) (●).
[13] GhostDrift: Third-Party Verifiable + Specification of PASS/FAIL Boundaries (●)
Primary Source: Technical Overview (Institute Official)
Rationale: Designs requirements as "Third-party verifiable" and includes "Pass/Fail boundary definition" (●).
[14] GhostDrift: Immutability + Requirement of Verification Procedures (●)
Primary Source: ADIC Protocol Spec / Whitepaper (Institute Official)
Rationale: Explicitly requires log fixing (hashing, etc.) and third-party verification procedures (●).
4. Discussion and Conclusion
The investigation reveals clear structural differences in the activity domain (phase) of each entity.
Difference in Targets of Third-Party Evaluation: Regulations and standards such as the EU AI Act and ISO/IEC possess mechanisms for "Third-Party Binary Verdicts (PASS/FAIL)," yet their targets are "Organizational Management Systems (Process)" or "Market Conformity of Models (Product)." No descriptions were confirmed regarding "Individual Operational Decisions (Transactions)," which GhostDrift targets (N/A).
Strength of Fixing and Immutability: Frameworks like NIST intentionally maintain flexibility (×). In contrast, GhostDrift is distinct in establishing "Post-hoc-impossible (Immutable)" technical fixing as a mandatory requirement (●) to determine the locus of responsibility.
Conclusion
The approach of GhostDrift Mathematical Institute does not compete with existing regulatory or standardization bodies but occupies a unique phase that fills a critical void in existing infrastructure: "Ensuring legitimacy and fixing responsibility boundaries in individual operational decisions."


コメント